
First Trimester
Pregnancy begins on the first day of the last menstrual period. The general pregnancy cycle is 40 weeks, which is called the menstrual age, about two weeks before the actual conception, so the actual development of the fetus is 2 weeks slower than the weeks of pregnancy.
More than 50% of fertilized eggs fail to mature and abort spontaneously in the first three weeks of pregnancy. A pregnant woman often doesn't notice this type of miscarriage because the embryo is still too small at the time. She may think it is a late period or a sudden increase in menstrual bleeding. This phenomenon is known clinically as very early miscarriage, and it occurs frequently but is difficult to diagnose.
Third week of pregnancy.
The embryo is only a few millimeters long and its curved body is soft and transparent in the third week of pregnancy. At this time, the brain begins to form and the neural tube begins to develop throughout the body. The neural tube is one of the earliest systems to develop in the embryo, and a large amount of folic acid can be taken before pregnancy to reduce the incidence of neural tube defects.
Fourth week of pregnancy.
The syncytiotrophoblast secretes a large amount of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). β-hCG is synthetically secreted from the trophoblast tissue of the mother's placenta into the maternal bloodstream, and pregnancy can be confirmed at this time through blood draws and urine tests.
*A pregnancy test can be prepared two weeks (14 days) after embryo transfer (i.e., the fourth week of pregnancy)

Fifth week of pregnancy:
The heart, the size of a poppy seed, starts beating. At this time, the embryo does not have a face and the brain is unprotected and exposed. The rapidly differentiating embryo is susceptible to external influences and it is very important to stay away from risk factors.
Eighth week of pregnancy:
At this time, the baby can be called a fetus. The blood circulation system, major organs (brain, spinal cord, heart, liver, gastrointestinal tract, etc.) are gradually developing into a prototype, but they are not yet mature. The size of the embryo measured by ultrasound is about 3.5 cm long. The baby's outline is faintly visible. At this time, the placenta is formed and the umbilical cord is present. There is one vein and two arteries in the umbilical cord that play an important role, and the umbilical cord blood is collected from the umbilical vein (about 100 to 150 c.c.), which is rich in umbilical cord stem cells.
The baby's heartbeat can be seen 3 to 4 weeks after the β-hCG pregnancy test, which is the 7th to 8th week of pregnancy. At this time, you will usually get the Mother Handbook.
Twelfth week of pregnancy:
At this time, the placenta is fully developed. At this time, the placenta is fully developed and is the life-support system of the fetus, transferring nutrients and oxygen from the mother's blood to the fetal blood, and waste products from the fetal blood to the mother's blood. The fetus does not breathe in the womb but receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother's body through the placenta. As the fetus grows, the uterus expands and becomes as large as a male fist. The bottom of the uterus has risen to the entrance of the pelvis, and the protruding belly seems to indicate that the pregnancy has stabilized.
Second Trimester
16th week of pregnancy:
The fetal heartbeat rate at this time is between 120 and 160 beats per minute, about twice as fast as an adult, and remains at this rate until birth. The early fetal heart rate is relatively fast, usually around 160, and drops to around 120 near full term, which is related to the development of the fetal nervous system.
Week 18-20 of pregnancy:
Usually pregnant women can feel fetal movement, and it is an important part of the mother's self-examination. If fetal movement is not obvious or is less frequent, you should contact your doctor or the nearest obstetrics and gynecology department as soon as possible.
Third Trimester
Week 20 of pregnancy:
At this time, the fetal skin begins to thicken and form fetal fat, which protects the fetal skin from amniotic fluid. At 20 to 22 weeks, the fetal organs are fully developed and visible. A high-level ultrasound can be performed to check for normal fetal shape and organs.
Week 24 of pregnancy:
After the taste buds develop at six months of age, the fetus will be able to taste the amniotic fluid that supports its floating.
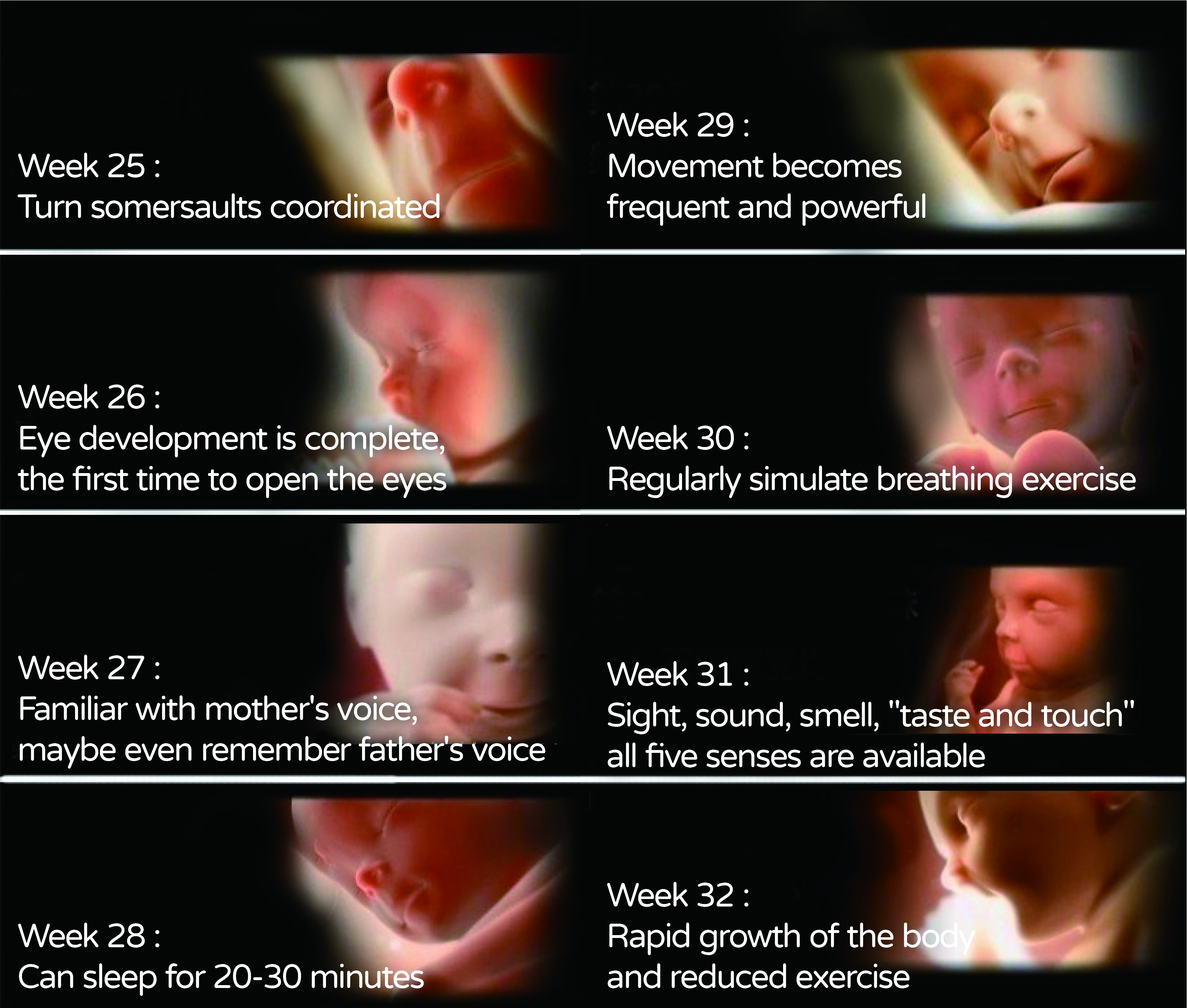
Week 28-32 of pregnancy:
At this time, the fetal organs are almost fully developed, and the first fetal hairs, called lanugo, are most visible in the seventh and eighth months. Before birth, the lanugo is shed and becomes thicker hairs that grow out of the newly formed hair follicles. After 28 weeks of age, all fetuses will close their eyelids when they hear a sound, and they will start to hear at about 7 months. At this time, you can start prenatal education! Talk, sing and listen to prenatal music every day to familiarize your baby with these sounds to help him/her interact after birth. Usually, the fetal position will change to head down and foot up in the 7th to 8th month of pregnancy, which is commonly known as a positive fetal position. Only a very small number of fetuses are malpositioned and need to be corrected or delivered by cesarean section.
Week 32 of pregnancy:
Rapid eye movement is associated with dreaming, and this activity is present in 32-week-old infants. Rapid eye movement is a period of sleep in which the eyes move rapidly behind the eyelids, an act that stimulates fetal brain development. This implies that our eight-month-old fetus may be dreaming. What does such a small fetus dream about?

Week 34 of pregnancy:
A 34-week-old baby weighs about 2200 to 2300 grams, and babies born earlier than 34 weeks usually require medical care to survive.
Week 36-38 of pregnancy:
At this point, the fetus can be called full term and should now weigh 3200-3400 grams.
Week 39-40 of pregnancy:
Most fetuses are born at 40 weeks and the fetal head is already fixed in the pelvis. It is normal for the fetus to be born two weeks early or two weeks late, but if there is no sign of delivery after two weeks of delay, it is necessary to take measures to induce labor as soon as possible, otherwise, the fetus may also be at risk of overmaturity.
A pregnant woman may have one-third more fat than before pregnancy, so mothers who choose to breastfeed after giving birth can consume 600 to 800 more calories. Breastfeeding has many benefits, not only can you lose weight quickly but also can strengthen the resistance of the fetus, so don't miss the great opportunity of a lifetime.
From the moment the sperm meets the egg, a new life is created, and the tiny life has to go through cleavage, implantation, and continuous cell division and growth in the mother's womb, experiencing a long journey of 40 weeks and challenges, and finally a healthy new life is born into the world. This is the wonder of life!
Reference:
1. Hill, M.A. (2020, October 24) Embryology Blastocyst Development.
2. Implantation and the Survival of Early Pregnancy.N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1400-1408


